Electromagnetic
Therapies

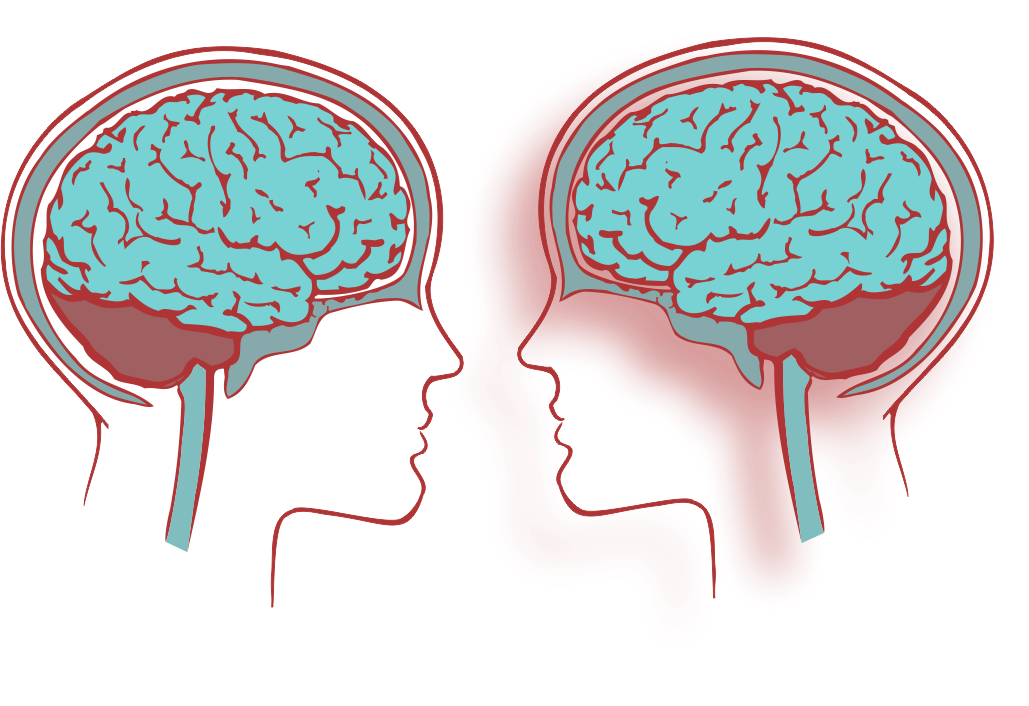
Differential Effects of Stroke Damage on Understanding and Speaking Language
Slide the green handle for responses to the question: "Are you going to visit your mother?"
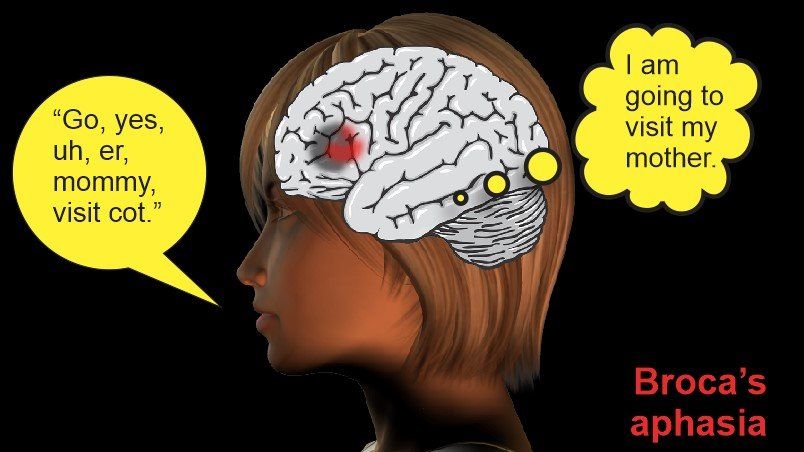
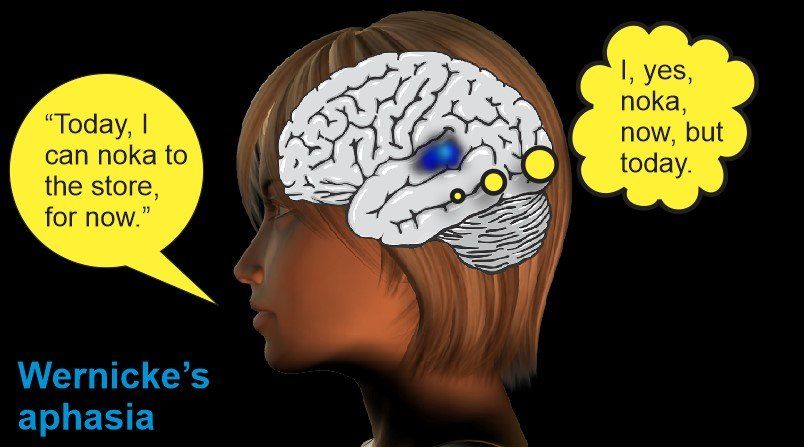
Those with damage to Wernicke’s area of the brain (in blue) cannot understand what others say to them. Those with damage to Broca's area (in red) cannot produce a coherent speech pattern.
The below videos show the effect of damage:
Electromagnetic
Therapies
Althought ECT has been used for decades to treat depression, it has been controversial. Some newer electromagnetic systems have produced results with simipler and less invasive solutions and with a wider range of use for disorders. Click on each below for videos explaining the procedures:
For more on this, see this NIH article: "Brain Stimulation Therapies."
Mirror Neurons
"Don't become a mere recorder of facts but try to penetrate the mystery of their origin."
Ivan Pavlov
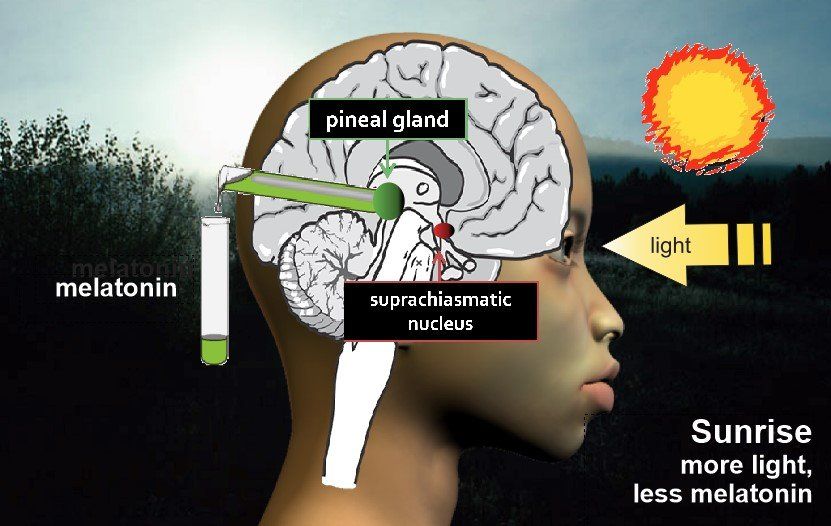
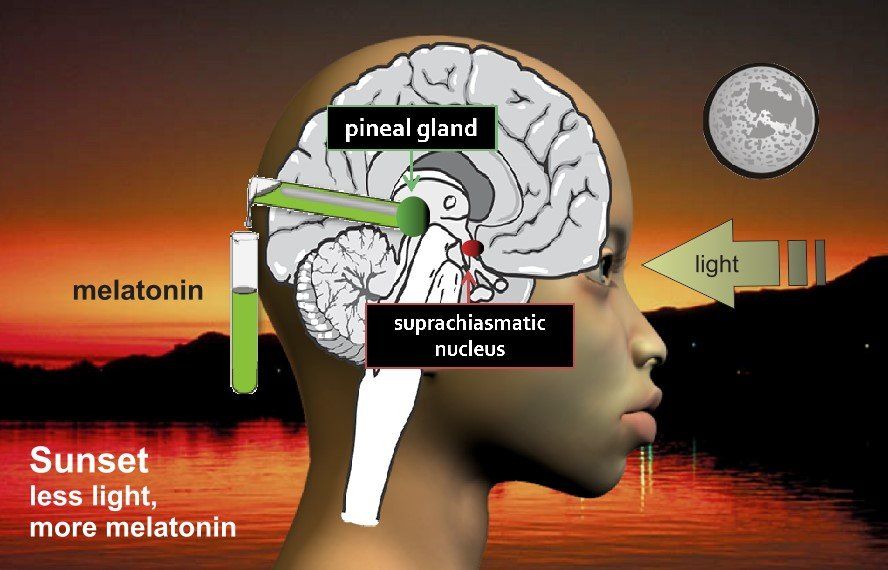
Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD)
SAD causes depression to increase in the winter months and subside during the summer months. One cause of this seems to be sensitivity to amounts of the hormone melatonin in the brain associated with sleep. Light through the eye affects the suprachiasmatic nucleus in the brain which then affects the pineal gland's production of melatonin.
Slide the red handle below to see how this all works and think how it might affect some during the shorter days of winter.