Applying Psych
ATTRIBUTION THEORY
Explaining the whys of our and others' behavior. To what do we attribute our and others' behavior.
Slide the Green Handles
Internal versus External Attribution


Fundamental Attribution Error


Actor-Observer Effect


Self-Serving Bias


POTENTIAL PROBLEMS WITH SPANKING
"The only person who is educated is the one who has learned how to learn - and change."
Carl Rogers
Types of Persuasion
Slide the white handle. Which is more effective?
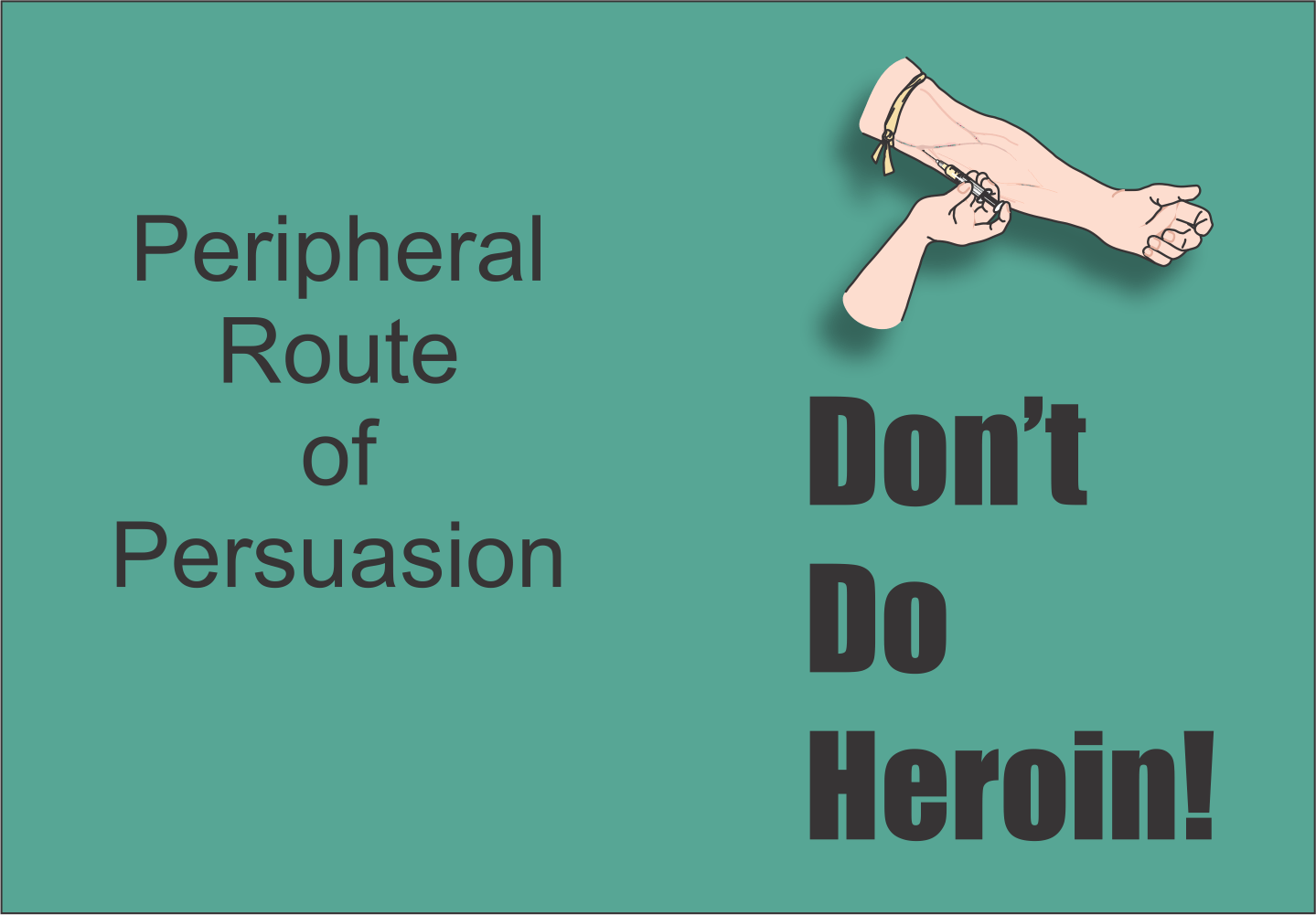
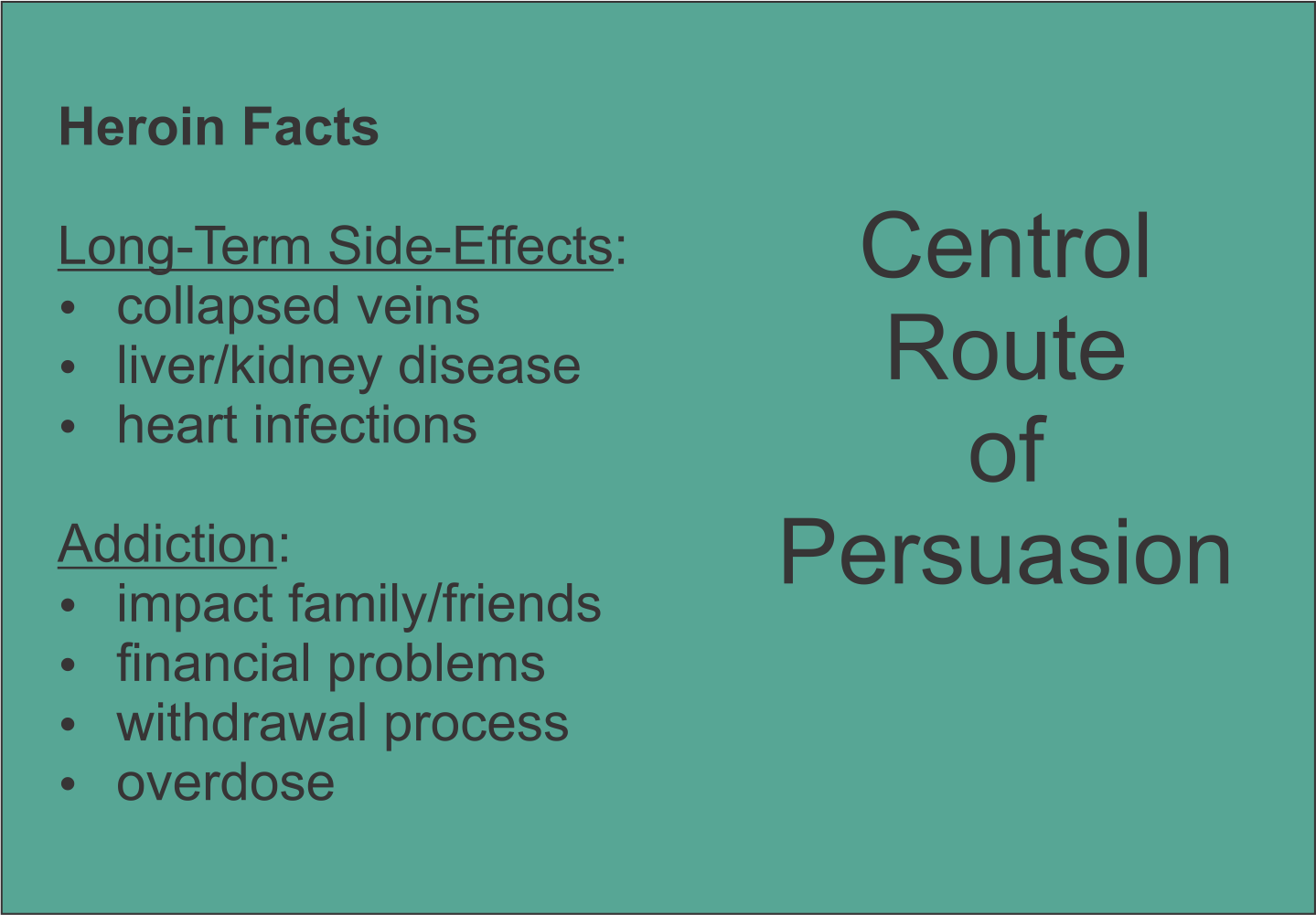
Social psychologists identify two types of persuasion: CENTRAL which influences by facts and arguments, and PERIPHERAL which influences by emotion. Research suggests the cental route produces more effective and longer-lasting attitude change.
